Rechargeable Battery Recycling Programme

Overview
To enhance public awareness in the recycling of rechargeable batteries, the Programme provides a Helpdesk Hotline (5575 4068) that is operated from 9:00 am – 6:00 pm, Monday to Friday. Property management / representatives of housing estates and buildings who are interested in participating in the Programme are welcome to call the Hotline for more information and application for registration.
Rechargeable batteries contain materials that can be hazardous to people and the environment in case of improper disposal. The best solution is to recover the valuable materials from the batteries and recycle them for use in other products, such as magnetic alloy and stainless steel.
Launched in April 2005, the Rechargeable Battery Recycling Programme (RBRP) is the first voluntary Producer Responsibility Scheme in Hong Kong. It has been set up and funded by the trade to collect and recover three common types of rechargeable batteries from household, which are Li-ion, Ni-MH and Ni-Cd.
You might be interested
What and Where to Recycle

What to recycle
Rechargeable batteries can be found in many electrical and electronic products. The RBRP mainly accepts all types of portable rechargeable batteries generated from household for recycling. Here is a list of some products that may contain dedicated rechargeable batteries:
- Mobile Phones
- Digital / Video Cameras
- Notebook Computers
- Power Tools
- Electronic Dictionaries
- Portable Vacuum Cleaners
- Electronic Game Sets
- Power Banks
Batteries for other household equipment not listed here are also suitable for recycling, provided they are portable rechargeable batteries.
How to recycle
Here's what you need to do before recycling rechargeable batteries:
- Remove the rechargeable battery from the equipment.
- For safety reason, cover the battery terminal with masking tape to prevent contact between terminals or other metal surfaces during storage and transport.
- Do not put damaged rechargeable batteries into the collection boxes. For batteries that are vulnerable to damage, put them in a plastic bag (e.g. re-use the packaging of new batteries) and seal them with adhesive tape before deposit.
- Bring the battery to a Collection Point for recycling. For operational considerations, the collection box may not be able to be placed in a prominent location of a Collection Point. Please approach the front-line staff or the manager of the respective Collection Point for details.
Where to recycle
Treatment of Rechargeable Batteries
What happens to the deposited rechargeable batteries
The deposited batteries are collected on a periodic basis, sorted and treated preliminarily according to battery type, stored and exported for recycling.
Battery Recovery and Recycling Flow Diagram

How rechargeable batteries are recycled
Rechargeable batteries contain materials of good value that can be recovered and re-used. For example, the Cobalt (Co) in Lithium Ion batteries can be used in magnetic alloy. Nickel (Ni) and Iron, from Nickel Metal Hydride and Nickel Cadmium batteries, can be used in stainless steel; the Cadmium (Cd) can be used to make new rechargeable batteries. It therefore makes good economic sense to recycle rechargeable batteries.
 Co Oxalate |  Ni-Ingot |  Stainless steel plate |  Cd-Ingot |
Another reason to recycle is that some materials in rechargeable batteries, such as cadmium, are also hazardous to human health and the environment. It's better to properly collect and recover these materials rather than risk them seeping into the environment.
The Recycling Process
Discharge (For lithium ion battery scraps only, to avoid potential hazard during the recycling process) Crush 1 (To break the plastic cases) Sort Plastic and Battery (To separate plastic materials from the batteries) Crush 2 (To crack the surface of batteries for effective heating) Melt (In an electric vacuum furnace) Final Product Packing | 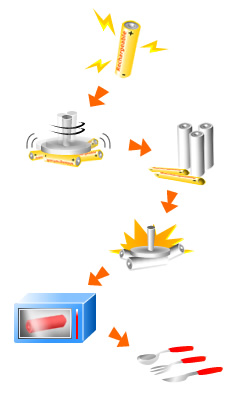 |
Join Now

Housing Estate and Commercial/Industrial Building

A convenient collection point can make all the difference in recycling. If it's located near your home or workplace, it's a lot easier to participate. All housing estates and commercial / industrial buildings are encouraged to join the Programme and set up collection points. The Programme will provide collection boxes, publicity materials and detailed guidance information to participated housing estates and buildings. Interested property management / representatives of housing estates and buildings can submit the completed Application Form, or call the Hotline (5575 4068) for more information.
Schools

The Programme also provides a Rechargeable Battery Recycling Programme Education Kit, which includes a poster, CD-ROM game, two game boards and colour worksheets for promoting rechargeable battery recycling in schools. Interested schools can submit the completed Application Form, or call 5575 4068 for more information.
Participating Companies and Organisations
Producers and importers of rechargeable batteries and electrical / electronic equipment have a shared responsibility to recycle post-consumer batteries. The RBRP is currently supported and funded by suppliers, importers and retailers of rechargeable batteries and electrical / electronic equipment. The Hong Kong Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Recycling Association is the Programme Manager while EPD serves as the Programme Advisor by providing advice and support to the Programme and promoting the RBRP to the public.
Member Companies
The following companies currently support and fund the Programme:
| Company | Brand |
|---|---|
| Procter & Gamble Hong Kong Limited | Braun, Oral-B |
| Canon Hong Kong Company Limited | Canon |
| CSL Mobile Limited | CSL |
| CLP Power Hong Kong Limited | CLP |
| Shun Hing Electronic Trading Co., Ltd. | Eneloop, Panasonic |
| Epson Hong Kong Ltd | Epson |
| GP batteries international limited | GP |
| Hong Yip Service Company Limited | Hong Yip |
| Techtronic Asia Company Limited | Milwaukee |
| Momax Technology Hong Kong Limited | Momax |
| Shun Tak Property Management Ltd. (The Westwood) | The Westwood |
| X Power International Trading Ltd. | X Power |

If your company would like to support the Programme, please submit the completed Reply Slip. The RBRP Helpdesk will contact you with further details.
Supporting Organisations
The following companies are also supporting the Programme, for example by providing collection points at their retail outlets and stations:
- 7-Eleven
- AEON Stores (Hong Kong) Co., Ltd.
- China Mobile Hong Kong
- FORTRESS
- Hong Kong and Kowloon Ferry
- Inchcape HK Group
- McDonald's
- MTRC
- Pricerite
- The Boys' & Girls' Clubs Association of Hong Kong
- Watsons the Personal Store
- Wellcome
Government Departments and Non-Government Organisations
- Business Environmental Council
- Environmental Association
- Environmental Protection Department
- Friends of the Earth
- Green Power
- World Green Organisation
Find Out More
Useful Contacts
· RBRP Helpdesk Hotline: 5575 4068
· Email: vprs_helpdesk@hkpc.org
What’s the difference between Rechargeable and Primary Batteries?

Primary Battery Types
| Type | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Zinc Carbon | Commonly used in daily applications. Not suitable for devices that require high current. |
| Alkaline Manganese | Commonly used in daily applications. Longer service life than Zinc Carbons. |
| Lithium | Usually used in light weight electronic devices. |
| Silver Oxide | Button cells |
| Zinc Air | |
| Alkaline |
Secondary Battery Types
| Type | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Nickel Cadmium (Ni-Cd) | (i) Can be recharged for 500-1000 times. (ii) Perform better on "heavy continuous drain" devices. |
| Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) | |
| Lithium Ion (Li-ion) | |
| Lead Acid* | Usually used as car batteries and backup power supply. |
*Note: The RBRP only accepts and recycles rechargeable batteries generated from households, including Li-ion, Li polymer, NiMH and NiCd but does not cover lead acid batteries. Lead acid batteries generated from commercial and industrial premises should be handled as chemical waste under the Waste Disposal (Chemical Waste) (General) Regulation.
Rechargeable VS Primary Batteries
| Rechargeable Battery | Primary battery | |
|---|---|---|
| Long Term Cost |  |  |
| Amount of Battery Waste Generated |  | |
| Recycling Cost Effectiveness |  |  |
Why don't we recycle disposable batteries?
The recycling of primary batteries has far fewer environmental and economic benefits than recycling rechargeable ones. Due to the fact that only tiny amount of low-value materials, such as iron, zinc and manganese could be recovered from recycling of primary batteries. Furthermore, the relevant recycling facilities are mainly located in overseas countries. Export to overseas countries for recycling would involve much higher recovery cost and carbon footprint.
In general, primary batteries contain less hazardous metals than rechargeable ones, especially since governments started restricting their mercury content. In addition to this, Hong Kong is equipped to safely dispose of batteries. Our strategic landfills are lined with impermeable liners to ensure there will be no untreated discharges to the environment. Nonetheless, rechargeable batteries remain the best choice as they can be re-used hundreds of times and are more cost-effective to recycle and create less waste.


